|
Creating Curves or Framework
Curves are spline line segments controlled by CVs. Curves are the framework of shapes. CVs (or control vertices) are the points which control and make up the line curve. These lines are called NURBs (non-uniform rational b-splines). NURBs are special because they form smooth curves between CVs.
Select the Modeling section of Maya.
Choose Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool->
Click on Curve Degree
3 Cubic for rounded curves
1 Linear for straight curves.
Click the mouse to input CVs in any view to create a curve.
Four points need to be input for Cubic curves.
Hit Enter button on the keyboard when you are finished.
Choose Curves->Open/Close Curves (This will close an active curve.)
Custom Shelf
Add tools you commonly use to the Custom Shelf.
PC: Hold down Shift + Ctrl keys while selecting a tool such as Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool
Mac: Hold down Shift + Command keys while selecting a tool such as Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool
Double click the icon to see the options for the tool.
(Use Windows->Settings/Preference->Shelf Editor to remove items from the shelf.)
Combining straight and rounded curves
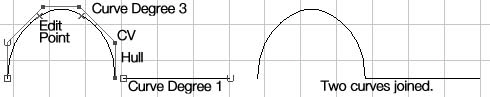
Choose Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool->
Select Curve Degree 3 Cubic to draw the rounded curve
Hit the Return button on the keyboard to finish the curve.
Choose Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool->
Select Curve Degree 1 Linear to draw the straight curve
Hit the Return button on the keyboard to finish the curve.
Select the round Cubic curve, then use Shift and select the straight Linear curve.
Use Curves->Attach->
Choose Attach Method Connect
Uncheck Keep Originals
Click Attach
Use Edit->Delete by Type->History
This will delete the construction history. The history gets in the way of moving the curve.
Grid Snap Option x
This option snaps CVs and object pivot centers to the nearest grid location while inputting or transforming. This is useful when precision is required. The Grid Snap button is located on the Status Line menu upper center.
Keyboard shortcut: Hold down x while transforming an object or CV. 
Point Snap, Lock CVs to visible CVs v
This option snaps CVs and object pivot centers to visible CVs or edit points.
Select the object to snap to.
NURBs
Use Display->NURBS->CVs, this will make the CVs visible for selected NURBs objects.
Polygon Mesh
Use Display->Polygons->vertices, this will make the points visible for active polys.
The Point Snap button is located on the Status Line menu upper center.
Keyboard shortcut: Hold down v while transforming an object or CV 
Curve Snap c
Curve Snap allows you to move objects, pivots or points along a curve or object.
The curve Snap is located on the Status Line menu upper center.
Keyboard shortcut: hold down c while transforming an object or CV. 
The cursor needs to be close to the curve in order to work.
Add CVs to Existing NURBs Surface
This function allows you to input a row of CVs in-between existing isoparms on 3D surfaces.
Isoparms are the lines on the NURBs surface.
In object type  mode, select the NURBs surface in which you would like to add a row of CVs. mode, select the NURBs surface in which you would like to add a row of CVs.
Move the mouse over the object.
Hold down the right mouse button to bring up the object menu.
Select Isoparm.
Click and drag on one of the existing isoparms with the left mouse button to move a copy of the isoparm over the surface of the object. (Hold down shift to select more than one isoparm.)
Select Surfaces->Insert Isoparms to complete the process.
Detach
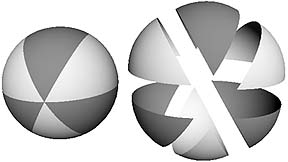
This function allows you to cut a NURBs surface along an isoparm.
(It can also break a curve at an edit point.)
This section might be easier in wireframe mode. Select a view, hit 4 to switch to wireframe.
In object type  mode, select the NURBs surface you would like to detach. mode, select the NURBs surface you would like to detach.
Move the mouse over the object, hold down the right mouse button to bring up the object menu, select isoparm, Click on one of the isoparms with the left mouse button to select it.
Select Surfaces->Detach
Invisible Ctrl h
This function allows you to make an active object invisible.
Select all objects to turn invisible.
Choose Display->Hide->Hide Selection or Ctrl h
To turn your object visible:
Choose Display->Show->All etc
Give a Curve a Planar NURBs Surface
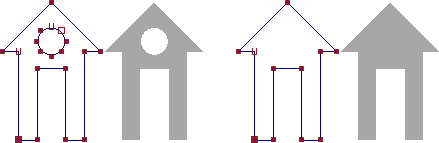
Curves are framework, they have no surface. Use Planar to surface flat curves. The closed curves will use a function called trim to cut out regions on an invisible plane.
Use Curves->CV Curve Tool->
Draw one or more curves, place one inside of the other.
If the curve does not form a closed shape, you could select Curves->Open/Close Curves
Select the outer curve first, then select the rest
Choose Surfaces->Planar
Curve to Flat Polygon Mesh with Bevel Plus
This creates something similar to planar surface, the geometry may be cleaner for polygons.
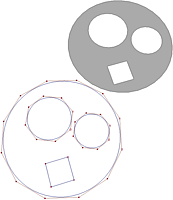
Choose Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool->
Click on Curve Degree 3 Cubic for rounded curves, or use 1 Linear for straight curves.
Draw the outer curve.
Hit Enter button on the keyboard when you are finished.
If you need to, choose Curves->Open/Close Curves to close, or make sure the first point is on top of the last point (use v point snap)
Add holes if you like.
Select the curve(s), outer curve first
Choose Surfaces->Bevel Plus->
Under Bevel tab:
Create bevel: Check At start, uncheck At end
Bevel width: 0
Bevel depth: 0
Extrude distance: 0
Create cap: Check At start, uncheck At end
Under Output Options tab:
Output geometry: Polygons
Tessellation method: Sampling
Under Sampling Controls:
Along extrusion: Section
Samples: 1
Along curve: Span
Samples: 1 For Linear curve input 1, for Cubic curves input 3 or more.
Click Bevel
Select the model and run Mesh->Cleanup...->
Select Lamina faces (faces sharing all edges)
This will get rid of all double surfaces.
Select the model and run Edit Mesh->Merge->
Make sure the Tolerance is very small .00001
Revolve
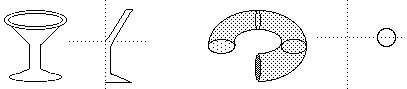
Revolve will lathe a cross-section around the pivot center, a certain number of degrees.
Input a profile curve in the front view up against the Y axis. (Later you may use any view.)
Select the curve.
Choose Surfaces->Revolve->
Select Axis Preset Y
Select End Sweep Angle 360 (Number of degrees curve will sweep around.)
Select Segments 6 (Resolution of the sweep.)
Click on Revolve
Extruded Surfaces with a Curve Path
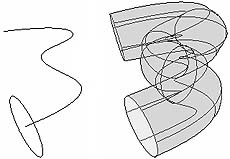
This tool will sweep a curve along a path.
Draw a curve to be used as a cross-section.
Draw a path.
Orient the cross-section centered and perpendicular to the path.
Select the cross-section and then the path
Select Surfaces->Extrude->
Choose Style Tube
Choose Result Position At Path
Choose Pivot Closest End Point
Choose Orientation Profile Normal
Choose Curve Range Complete (This can be used for animating a write-on later.)
Choose Output Geometry NURBs
Try out the various options, compare the differences.
Extruded Surfaces with a Profile, using Distance
Draw a curve in the any view, for now use the front view.
Select the curve.
Select Surfaces->Extrude->
Choose Style Distance
Input your Extrude Length
Choose Direction Specify
Choose the Z Axis
Click Extrude
Duplicate Existing Curves
This function lets you make an exact duplicate of an isoparm from a surface.
In object type  mode, select the NURBs surface you would like to duplicate a curve from. mode, select the NURBs surface you would like to duplicate a curve from.
Move the mouse over the object, hold down the right mouse button to bring up the object menu, select isoparm. Click on one of the isoparms to select it.
Use Curves->Duplicate Surface Curves to make a new curve from the active isoparm.
Connect Cross-sections with Loft
In the front view draw two or more curve cross-sections. (This will work in any view.)
Place the cross-sections in different positions along the z axis. (This works with any axis.)
Hold down the Shift key and select all the curves or isoparms in order.
Use Surfaces->Loft (This will connect the cross-sections.)
Offset Curve
Draw a NURBs curve, Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool
Select Curves->Offset->Offset Curve
Input a positive or negative Offset distance.
Any NURBs Tool can be used to create Polygons
Switch over to the Modeling section, choose from upper left, status line.

Draw a couple NURBs curves, Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool
Select Surfaces->Loft->
Choose Polygons
Choose Quads
Choose Tessellation method: General
Change U type to: Per span # of iso params
Change V type to: Per span # of iso params
Input Number U: 3 (If this is too jaggy, increase)
Input Number V: 1
Hit Apply
Use Mesh Display->Harden Edge if the shading appears incorrect.
Use Mesh Display->Reverse if the object is inside out, it will appear black.
Fix Poly Texture Loft issue
If you are texture mapping a loft shape, you may want to try:
Draw a couple NURBs curves, Create->Curve Tools->CV Curve Tool
Select Surfaces->Loft->
Choose Polygons
Choose Quads
Choose Tessellation method: General
Change U type to: Per span # of iso params
Change V type to: Per span # of iso params
Input Number U: 1 (If this is too jaggy, increase)
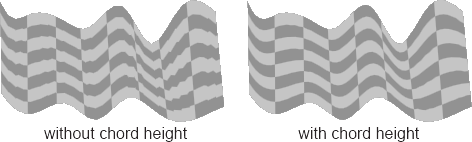
Input Number V: 1
Select Use chord height
Hit Apply
This will add more polygons.
Poly Mesh
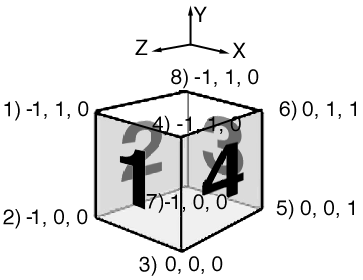
A polygon mesh object is made of polygons. The illustration above indicates the 4 polygons that make up the cube. A polygon is a closed planer surface. The smoothness of an object depends on the number of polygons defined.
A list of data points for the polygon mesh above may appear as follows:
List of vertices and their number.
1) -1, 1, 0
2) -1, 0, 0
3) 0, 0, 0
4) 0, 1, 0
5) 0, 0, 1
6) 0, 1, 1
7) -1, 0, 0
8) -1, 1, 0
List of polygons and the vertices that construct them.
1) 1, 2, 3, 4
2) 1, 2, 7, 8
3) 8, 7, 5, 6
4) 5, 6, 4, 3
NURBs Surface
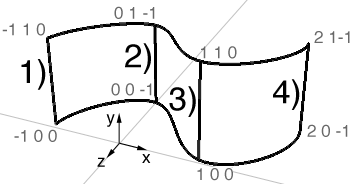
A NURBs surface is made of parametric cubic curves. In other words, lines connect to form a continuous grid like surface.
A list of data points for a patch may appear as follows:
List of vertices and their edge number.
|
|
-1, 0 0
-1, 1, 0
0, 0, -1
0, 1, -1
1, 0, 0
1, 1, 0
2, 0, -1
2, 1, -1
|
|
|
|
|
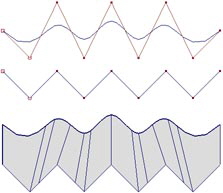
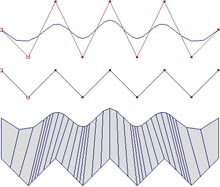
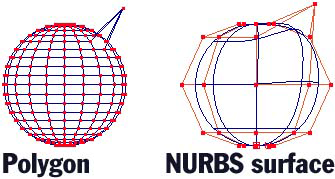
Each point is connected by a straight line.
Many points are needed to make a smooth curve.
|
Points are connected by curved splines.
A few points can define a smooth curve.
It is easy to create smooth curved surfaces.
Can adjust the subdivisions to make the surface more round.
Can be converted into a polygon mesh.
|